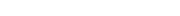


The company strictly implements incoming materials testing, comparison of incoming materials, screening and inspection of raw...
The company's superior geographical location and lean management team reduce transportation and labor costs; through strict control...
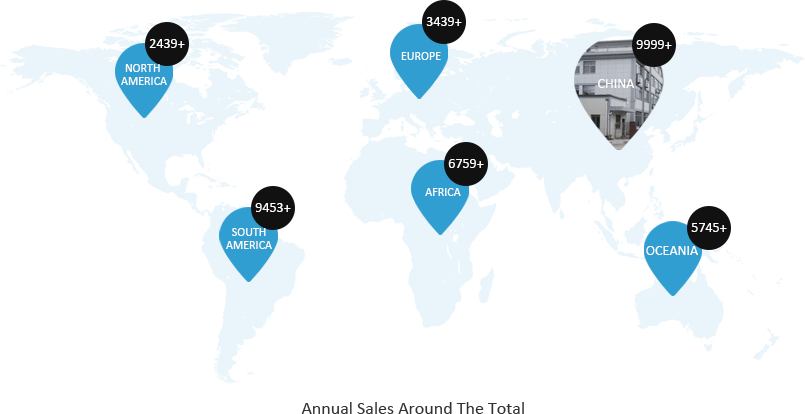
Our company has ample production capacity and full control over raw material prices, quality, and stable supply, laying the foundation...
Our company has consistently adhered to a seamless docking service, carefully created a service team consisting of technical backbones...
Professional Wash Motors Manufacturer
The standing fan motor is the core component of both household and commercial fans. During operation, it may experience overheating, which can affect motor...
15 Dec, 2025The standing fan motor is the core component of both household and commercial fans, directly affecting performance, durability, and user experience. Prolon...
08 Dec, 2025Spin motors, as a highly efficient and compact type of electric motor, have gained widespread application in industries such as electric vehicles, robotics...
01 Dec, 2025Power Density Advantages of Spin Motors Spin motors have emerged as a revolutionary technology in various industries, offering significant advantages over ...
24 Nov, 2025
We will get back to you within 12 hours on weekdays since we received the inquiry.
We are a professional electrical motor manufacturer, at the same time, we also have our own international trade department, we sell our own products.
We mainly produce washing machine motor, dryer motor, air conditioner motor, kitchen appliance motor, fan motor, air purifier motor, food processing machine motor and other several kinds of motors. At present, we have thousands of motor products, we focus on motor control, and also provide customers with specialized motor and systematized solution.
Our products almost cover the whole household appliance industry, mainly used in washing machine, air conditioner, kitchen appliance, fan, etc. We also provide motor for industry manufacturing equipment.
Yes, we mainly produce customized products. We develop and produce products according to blueprint or sample provided by customer. We can even customize a systematic program and design satisfactory products for our customers according to their opinions and requirements.
At present, our production capacity reaches 30000, annual productivity is more than 10 million.
We have an IQC department, quality will be guaranteed at the initial step. In production, there will be a corresponding test after every process, for the finished product, we will do IQC inspection according to the customer’s requirements and international standards; Then, we have advanced and completed top testing equipment and system: spectrum analyzer, 3D coordinate measuring machine, Motor comprehensive test machine and hysteretic dynamometer, etc. The above equipment can ensure to provision of high quality and high-performance final products for customers, at the same time, they also can satisfy customers’ all-round testing requirements of motor.
When offering, we will confirm the trading term with you, FOB, CIF, CNF, or any other terms. In mass production, we usually prefer payment terms like 30% prepayment, and 70% based on the on-board date. Usually, we do business by the payment term T/T, and of course, L/C is also acceptable.
Generally, we ship goods by sea, because we are in Huzhou City, 35km away from Shanghai port, which make the shipment delivery very convenient and economic both for us and customer. Of course, if customers’ goods are urgent, we also provide air delivery, Ningbo airport and Shanghai international airport are close to us.