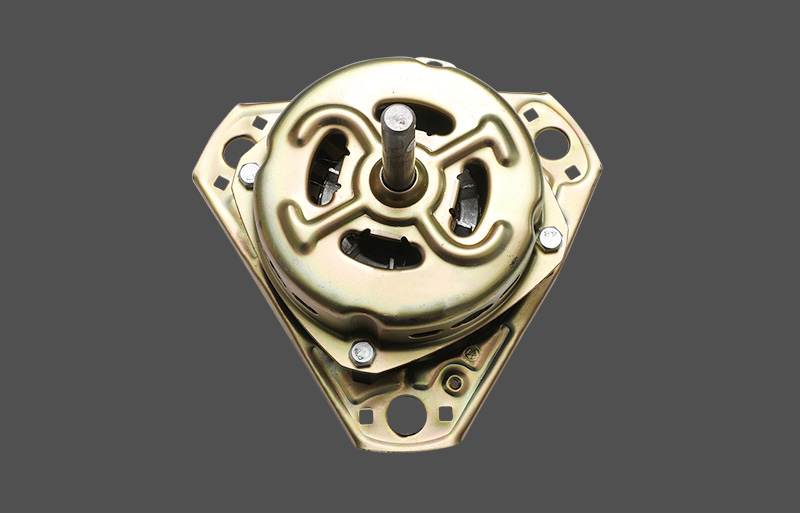
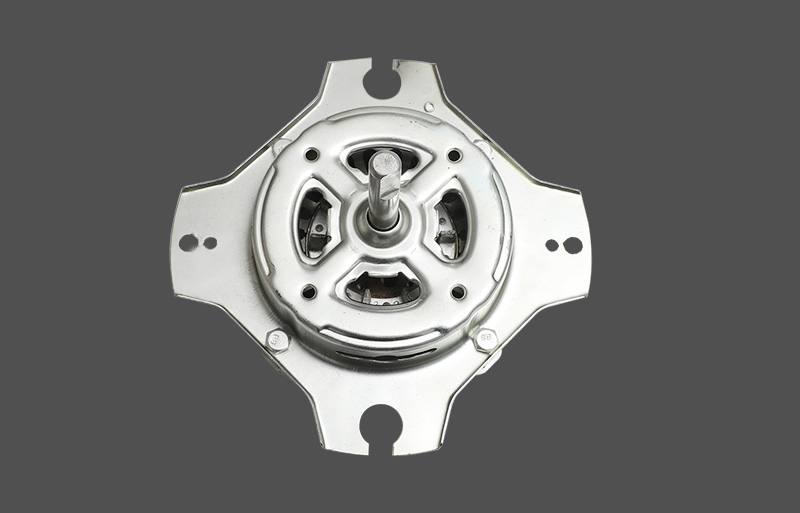
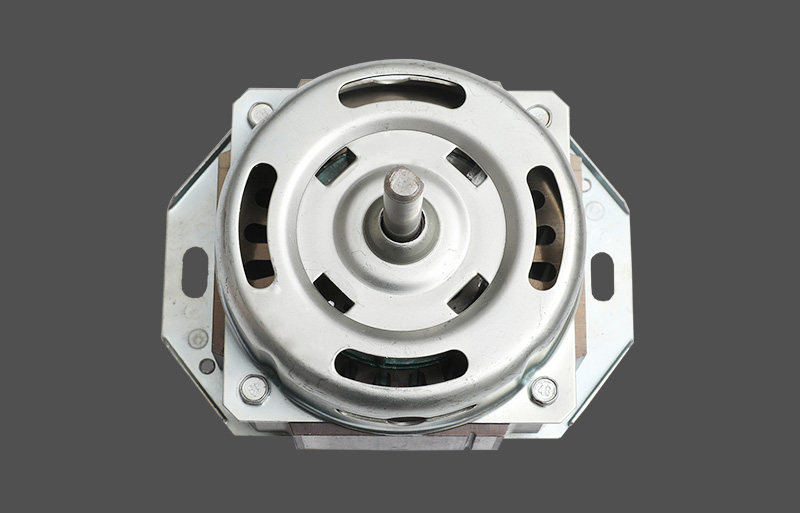
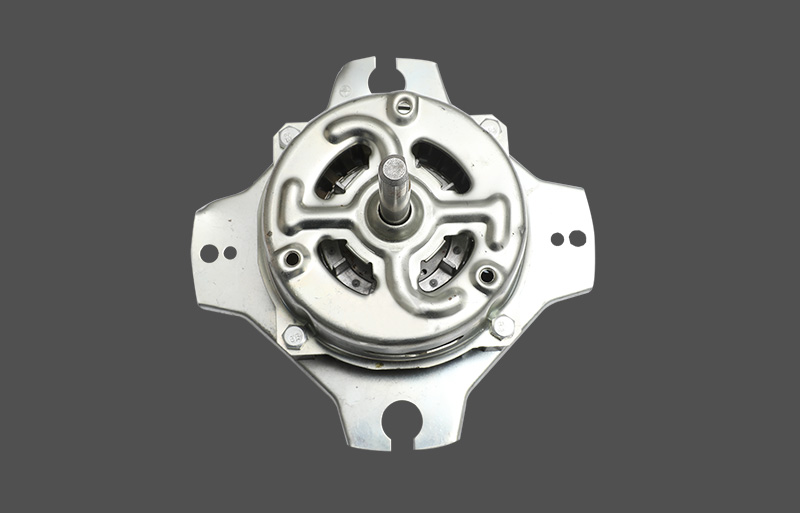
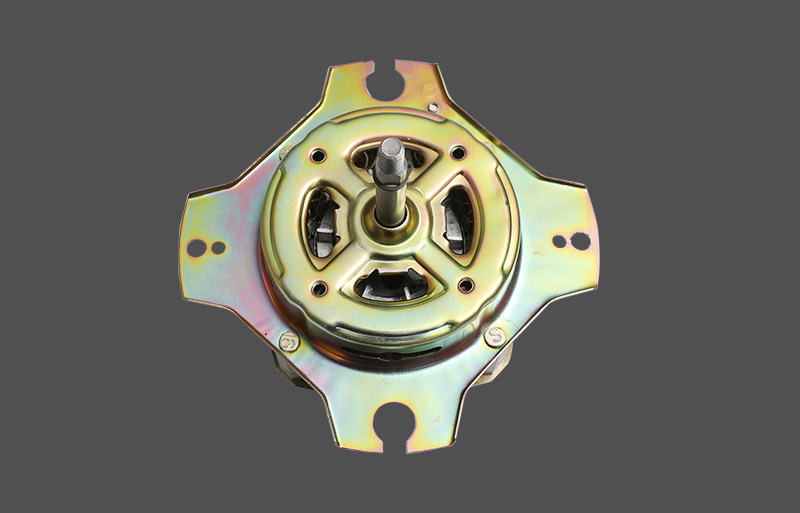
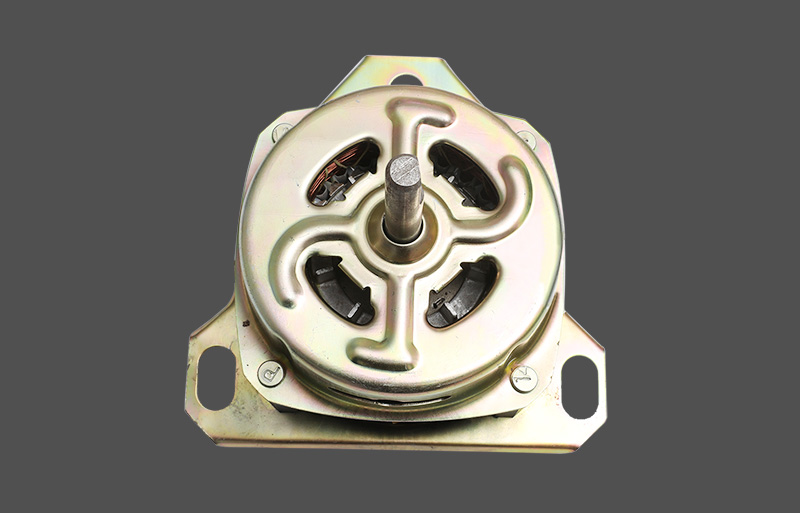
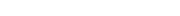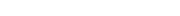The stator is used to generate a rotating magnetic field. The stator of a three-phase motor is generally composed of a casing, a stator core, a stator winding, and the like.
(1) outer casing
The three-phase motor housing includes a base, an end cover, a bearing cover, a junction box, and a lifting eye.
Base: cast iron or cast steel, its role is to protect and fix the statorWashing machine wash motors winding of the three-phase motor. The base of the medium and small three-phase motors also has two end caps that support the rotor, which is an important part of the mechanical structure of the three-phase motor. Usually, the appearance of the base requires good heat dissipation, so heat sinks are generally cast.
End cap: casted in cast iron or cast steel, its role is to fix the rotor in the center of the stator cavity, so that the rotor can rotate evenly in the stator.
Bearing cap: It is also cast iron or cast steel. Its function is to fix the rotor, so that the rotor can not move axially, and it also plays the role of storing lubricating oil and protecting the bearing.
Junction box: Generally cast in cast iron, its role is to protect and fix the lead terminal of the winding.
Lifting ring: It is usually made of cast steel and installed at the upper end of the machine base to lift and lift the three-phase motor.
(2) Stator core
The stator core of the asynchronous motor is a part of the magnetic circuit of the motor, which is formed by laminating a thin silicon steel sheet coated with an insulating varnish on a surface of 0.35 mm to 0.5 mm thick, as shown in Fig. 2. Since the silicon steel sheet is thin and the sheet is insulated from the sheet, the core eddy current loss due to the passage of the alternating magnetic flux is reduced. The inner circumference of the core has evenly distributed slots for inserting the stator windings.
a) stator core (b) stator punch
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of stator core and punching
(3) stator winding
The stator winding is the circuit part of the three-phase motor. The three-phase motor has three-phase windings, and when a three-phase symmetrical current is applied, a rotating magnetic field is generated. The three-phase winding consists of three independent windings, each of which is connected by a number of coils. Each winding is a phase, each winding differing in space by 120° electrical angle. The coil is wound by an insulated copper wire or an insulated aluminum wire. The medium and small three-phase motors are mostly round enameled wires. The stator coils of the large and medium-sized three-phase motors are wound with a large-section insulated flat copper wire or flat aluminum wire, and then embedded in the stator core groove according to a certain rule. The six outlet ends of the three-phase winding of the stator are led to the junction box. The first ends are labeled U1, V1, W1, and the ends are labeled U2, V2, W2. The arrangement of the six outlet ends in the junction box is shown in Figure 3, which can be connected in a star or a triangle.